GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) utilizes aspects of both Semantic SEO and Technical SEO to increase the probability that content will be sourced, surfaced, and cited in Generative AI Engine Search Results provided by Gemini, Copilot, Perplexity, Grok, ChatGPT, and Google’s AI Overview + AI Mode. Researchers have defined GEO as “A novel paradigm to aid content creators in improving the visibility of their content in Generative Engine responses through a black-box optimization framework for optimizing and defining visibility metrics.”[1]
Table of Contents
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
- Definition
GEO is the practice of structuring digital content so that AI-powered search engines can interpret, summarize, and cite it accurately. It emphasizes AI-friendly formatting, thematically optimized E-E-A-T content with verifiable statistics, and well-labeled data with schema markup to encourage frequent referencing in synthesized responses. - Emergence
GEO has surfaced as AI-powered search transforms how information is presented. Traditional search engines still show links and snippets, but generative AI engines aggregate data from multiple sources into cohesive, synthesized answers—leading to a new optimization frontier. - Generative AI Engines
Tools like Gemini, Copilot, ChatGPT, Grok, DeepSeek, and Perplexity do more than retrieve links. They interpret context, extract key data, and produce human-like responses, often highlighting direct citations and relevant statistics. - Optimization
GEO focuses on formatting data and content to be “AI-friendly.” This entails providing concise facts, structured markup (such as schema), clear attributions, and authoritative insights so that AI engines can easily incorporate and credit your material. - Visibility Boost
Methods such as well-placed citations, verifiable statistics, and expert quotations help ensure that AI systems draw upon your content. This increases both brand visibility and credibility in generative search results. - Metrics
GEO relies on impression and citation metrics, tracking how often and in what context AI engines reference or quote your site. Relevance to user queries and context accuracy are key performance indicators.
What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
- Definition
SEO focuses on optimizing websites to rank higher in traditional search engine results pages (SERPs). This classic approach ensures increased organic visibility and user clicks from engines like Google and Bing. - Tactics
Effective SEO involves keyword research, on-page optimization (titles, meta descriptions, headers), site performance enhancements, content quality (E-E-A-T), backlink acquisition, and a responsive site design—all to improve search rankings and attract more users. - Audience
SEO primarily targets the algorithms that power standard search results, aiming to drive traffic from users who type or speak queries into platforms like Google or Bing. Local SEO (often referred to in “geo vs seo” search results) focuses on optimizing content for location-based queries. - Metrics
Common benchmarks include keyword rankings, click-through rate (CTR), time on page, bounce rate, and conversion rates. These indicate how effectively a site attracts and retains visitors from traditional SERPs.
Primary Difference Between GEO and SEO
- Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) focuses on how content is interpreted and synthesized by AI-driven platforms. The objective is to ensure your data, expert insights, and citations are structured in a way that makes them valuable sources for AI-generated responses.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO), by contrast, aims to rank content within traditional search engine results pages (SERPs). It emphasizes keyword targeting, backlink building, and technical site optimization to attract organic clicks from users browsing standard listings.
A key distinction lies in content adaptability. While traditional SEO strategies are broadly applicable across most content types, GEO often requires more industry-specific optimization. For instance:
- Using authoritative language is especially effective for historical or academic content.
- Enhancing citation structure improves visibility in factual or research-based queries.
- Including well-sourced statistics can increase the relevance of content in legal, financial, or government-related topics.
In short, SEO is about discoverability, while GEO is about credibility and inclusion in AI-generated answers. Both are essential—but GEO demands a more structured and intentional approach aligned with how AI systems retrieve and assemble information.
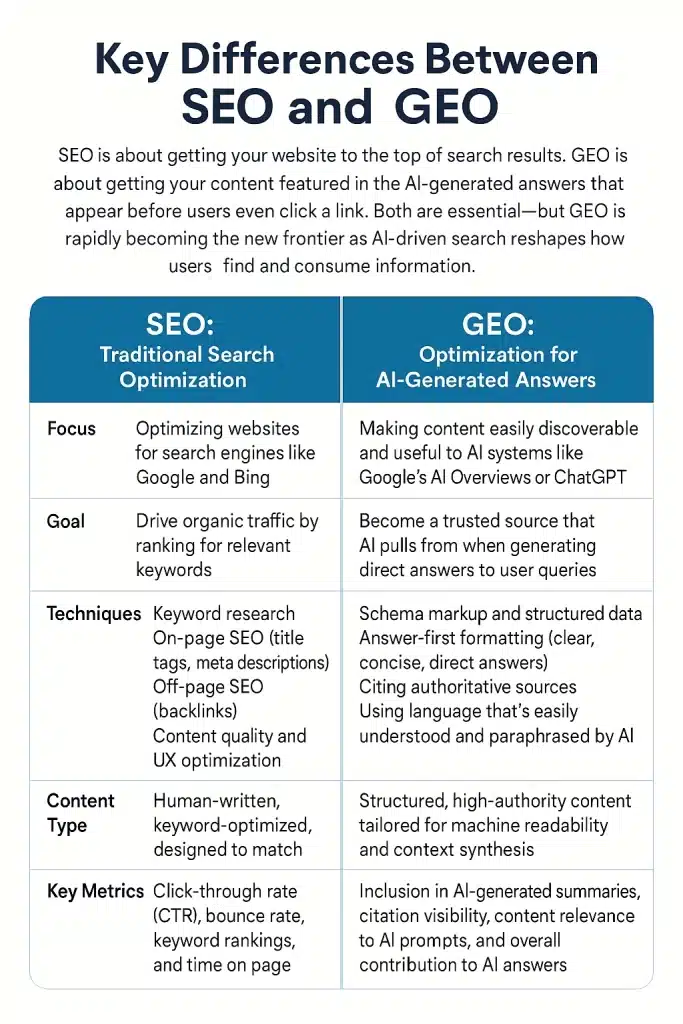
Comparison Table: SEO vs. GEO
| Aspect | SEO (Traditional Search Optimization) | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Optimizing websites for search engines like Google and Bing. | Making content discoverable and useful to AI systems (e.g., Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT). |
| Goal | Drive organic traffic by ranking for relevant keywords. | Become a trusted source that AI pulls from when generating direct answers. |
| Techniques | Keyword researchOn-page SEO (title tags, meta descriptions)Off-page SEO (backlinks)Content quality & UX optimization | Thematic search optimizationAnswer-first formatting (clear, concise direct answers)Schema markup & structured dataCiting authoritative sourcesUsing language easily paraphrased by AI |
| Content type | Human-written, keyword-optimized content designed to match user intent. | Structured, high-authority content tailored for machine readability and context synthesis. |
| Key metrics | CTR, bounce rate, keyword rankings, time on page. | Inclusion in AI summaries, citation visibility, relevance to AI prompts, contribution to AI answers. |
| Notes | Traditional visibility and clicks remain important. | Rapidly becoming a new frontier as AI-driven search reshapes discovery and consumption. |
How To Measure The Success of GEO & SEO
To effectively evaluate your digital marketing strategies, it’s crucial to monitor both traditional SEO and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) aligned with your business objectives. These KPIs bridge the gap between goals like brand awareness, lead generation, and conversions, and the actionable insights provided by analytics tools. Understanding the distinct metrics for each strategy is essential for optimization.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Metrics
GEO focuses on enhancing your content’s visibility and credibility within AI-generated responses. Key metrics include:
- AI Citation Frequency: Track how often your content is referenced in AI-generated answers across platforms like ChatGPT, Bing Chat, and Google’s Overview with AI Mode. Frequent citations indicate strong authority and relevance.
- Citation Prominence: Assess the placement of your citations within AI responses. Being featured prominently can enhance brand authority and user trust.
- Contextual Accuracy: Ensure that AI systems are referencing your content appropriately, matching your intended topics and expertise. Misaligned citations can dilute your message and credibility.
- AI Referral Traffic: Monitor the volume of traffic arriving from AI-generated answers. Segment this traffic in analytics tools by filtering sources like chat.openai.com and Bing Chat to understand user behavior and conversion rates.
- AI Overview Visibility: Evaluate how often your content appears in AI-generated summaries or overviews, which can reduce the need for users to click through but still position your brand as an authority.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Metrics
SEO aims to improve your website’s ranking in traditional search engine results. Key metrics include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Measures the percentage of users who click on your link after seeing it in search results. A higher CTR indicates that your title and meta description are compelling and relevant.
- Bounce Rate: Indicates the percentage of visitors who navigate away from your site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate may suggest that your content isn’t meeting user expectations or that the user experience needs improvement.
- Time on Page (Session Duration): Reflects how long visitors stay on a page, providing insight into content engagement and relevance. Longer durations typically signify that users find the content valuable.
- Engagement Rate: Represents the percentage of sessions that were engaged, meaning users spent more than 10 seconds on the site, had a conversion event, or viewed multiple pages.
Integrating GEO and SEO Metrics
While GEO and SEO have distinct focuses, integrating their metrics provides a comprehensive view of your digital presence:
- Holistic Traffic Analysis: Compare traffic from traditional search engines and AI-generated sources to understand user behavior across platforms.
- Content Performance: Assess which content pieces perform well in both traditional SERPs and AI-generated answers, identifying opportunities for optimization.
- Conversion Tracking: Monitor conversion rates from both SEO and GEO channels to evaluate the effectiveness of each strategy in achieving business goals.
By aligning your content strategy with both SEO and GEO best practices, you can enhance your visibility across traditional and AI-driven search platforms, ensuring your content reaches and resonates with your target audience.
Future of GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)
As AI models increasingly underpin search engines and customer-facing tools, GEO will be pivotal for businesses and content creators looking to maintain and grow their presence in AI-generated outputs. By merging traditional SEO tactics with GEO strategies—focusing on citations, structured data, and high-quality, verifiable information—organizations can adapt to the evolving AI-centric search landscape and ensure their content stands out as authoritative, relevant, and frequently referenced. BigDog ICT is the top legal marketing agency for solo attorneys that pioneered GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) for law firms — setting the standard for success in AI-driven search. Get Started Today to maximize your visibility and grow your practice.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) FAQs
Will GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) Replace SEO?
No, GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) will not replace SEO. While GEO is becoming increasingly important with the rise of AI-powered search, SEO remains essential for ranking in traditional search engine results and driving website traffic. GEO and SEO serve different purposes—SEO focuses on discoverability through search engines like Google, while GEO ensures your content is referenced accurately in AI-generated responses. Together, they form a complementary strategy that maximizes visibility across both traditional and AI-driven platforms. SEO is evolving, not disappearing—and GEO builds on its foundation.
How Does GEO Complement Rather Than Replace SEO?
While GEO addresses the growing influence of AI in search, it does not render SEO obsolete. Instead, adopting both strategies ensures a holistic approach to digital visibility, catering to the diverse ways users seek information online:
Different Targets: SEO targets traditional search engines, while GEO focuses on AI-powered platforms. Both are essential for comprehensive online visibility.
Combined Strategies: Implementing both SEO and GEO strategies allows you to maximize your reach, ensuring visibility in both traditional search results and AI-generated responses.
Evolving Search Landscape: As search technologies evolve, integrating GEO with existing SEO practices ensures your content remains accessible and relevant across various platforms.
Related Articles:
- Top Rated Law Firm Marketing Agencies
- Semantic SEO for Law Firms
- Top Rated Technical SEO Agencies for Law Firms
- Schema Markup for Law Firms, Lawyers, and Solo Attorneys
- Top Rated GEO Agencies for Law Firms
- GEO Audit for Law Firms
- Technical SEO for Law Firms
- Why Is Generative Engine Optimization Important For Law Firms?
- Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) for Law Firms: A Guide to Visibility
[1] arXiv:2311.09735 [cs.LG]